This post was published in 2021-10-03. Obviously, expired content is less useful to users if it has already pasted its expiration date.
主要内容:两个随机变量的函数的分布,多重积分换元法,正态分布,雅可比行列式/Jaccobi行列式/Jacobian/Jacobian determinant,(继续学习)二重积分,2维连续型随机变量,
两个随机变量的函数的分布
📚 《浙大概率论》 p76开始
设[mathjax](X,Y)[/mathjax]是二维连续型随机变量,概率密度为[mathjax]f(x,y)[/mathjax],则[mathjax]Z=X+Y[/mathjax]的概率密度为:[mathjax-d]\begin{gathered}f_{X+Y}(z)=f_{X} * f_{Y}=\int_{-\infty}^{\infty} f_{X}(z-y) f_{Y}(y) \mathrm{d} y=\int_{-\infty}^{\infty} f_{X}(x) f_{Y}(z-x) \mathrm{d} x \cr *: convolution\end{gathered}[/mathjax-d]
其中[mathjax]f_{X} * f_{Y}[/mathjax]是[mathjax]f_{X} [/mathjax]和[mathjax]f_{Y}[/mathjax]的卷积公式 .
(上述公式的证明过程在书上有)
🔗 http://staff.ustc.edu.cn/~zwp/teach/Prob-Stat/Lec8_slides.pdf
多重积分换元法
🔗 https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/171701301
正态分布
🔗 https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Normal_distribution
[mathjax-d]f(x)=\frac{1}{\sigma \sqrt{2 \pi}} e^{-\frac{1}{2}\left(\frac{x-\mu}{\sigma}\right)^{2}}[/mathjax-d]标准正态分布:
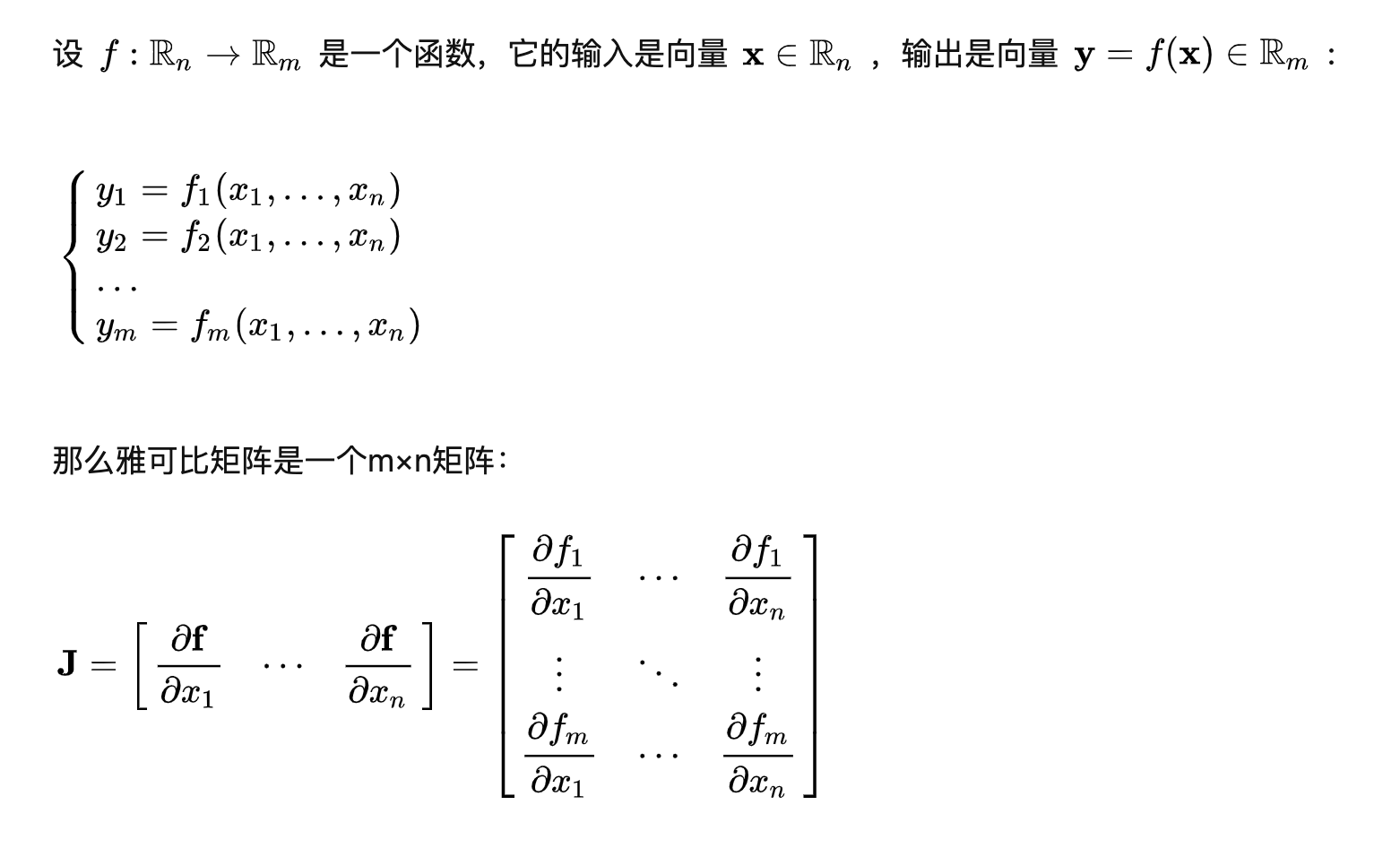
[mathjax-d]f(x)=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2 \pi}} e^{-\frac{x^2}{2}}[/mathjax-d]雅可比行列式/Jaccobi行列式/Jacobian/Jacobian determinant
🔗 入门讲解文章,附带了例题 https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/171701301
🔗 更一般化的文章,评论区里有学习Jacobian的其他资料推荐:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/39762178
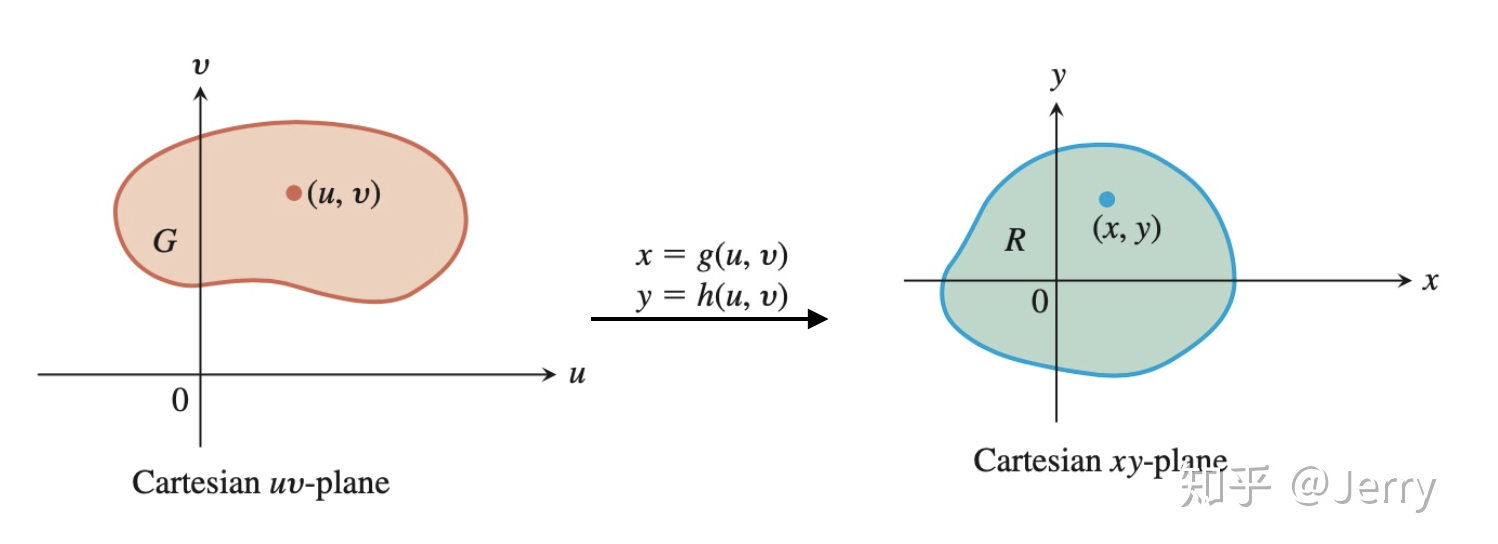
假设有从[mathjax](u,v)[/mathjax]到[mathjax](x,y)[/mathjax]的坐标系变换如下图所示:
那么定义一个雅可比行列式[mathjax]J(u, v)=\frac{\partial (x,y)}{\partial (u,v)}[/mathjax]:[mathjax-d]J(u, v)=\left|\begin{array}{ll} \frac{\partial x}{\partial u} & \frac{\partial x}{\partial v} \\ \frac{\partial y}{\partial u} & \frac{\partial y}{\partial v} \end{array}\right|=\frac{\partial x}{\partial u} \frac{\partial y}{\partial v}-\frac{\partial y}{\partial u} \frac{\partial x}{\partial v}[/mathjax-d]
所以这个坐标变换可以表示为:[mathjax-d]\iint_{R} f(x, y) d x d y=\iint_{G} f(g(u, v), h(u, v))\left|\frac{\partial(x, y)}{\partial(u, v)}\right| d u d v[/mathjax-d]
应用举例:
Jacobian从二维推广到多维:
🔗 https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/39762178 评论区有一些推荐的Jacobian学习资料,比如:
🔗 https://www.khanacademy.org/math/multivariable-calculus/multivariable-derivatives/jacobian/e/computing-the-jacobian (整个Jacobian章节)
Jacobian determinant :
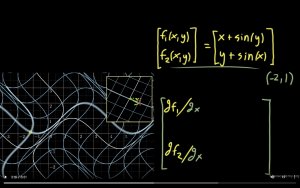
一个非常形象生动的例子,用[mathjax]det(J)[/mathjax]与[mathjax]1[/mathjax]的大小关系表示区域在坐标变换后的缩/放。如图所示,[mathjax]det(J)=0.46[/mathjax],所以区域[mathjax](0,1)[/mathjax]在坐标变换后面积缩小了。
(继续学习)二重积分:
(接昨天的)2维连续型随机变量
现在需要考虑这个情况:

🔗 中文名称:【随机向量函数的联合密度定理】, https://www.math.pku.edu.cn/teachers/lidf/course/probstathsy/probstathsy.pdf , P79
例题: 🔗 https://math.stackexchange.com/questions/2433685/let-x1-and-x2-two-independent-normal-distributions-compute-the-joint-distributi , 只有解题思路没有最后答案
例题:🔗 http://www.sfu.ca/~baa7/Teaching/02.joint-distributions 从第4页开始,有解体思路和最终答案